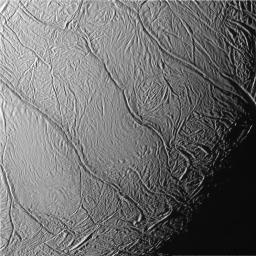
Press Release: Cassini Finds an Active, Watery World at Saturn's Enceladus
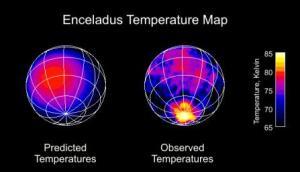
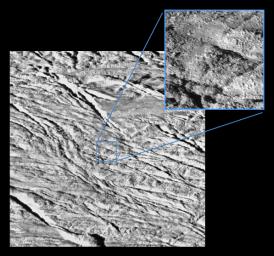
The CIRS data is the kicker. CIRS made temperature measurements both in dedicated scans and as ride-along observations with ISS. In both measurements, elevated temperatures were found in the south polar region near the tiger stripes and particularly within the tiger stripes. Color temperatures suggest that some areas in the tiger stripes could be as warm as 140K, indicating that the tiger stripes are regions of escaping internal heat. Such observations are indications that Enceladus is one of only three moons in the outer solar system with active volcanism (though the jury is still out with Titan, no elevated surface temperatures have been found there).
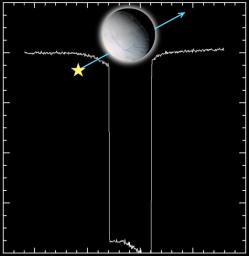
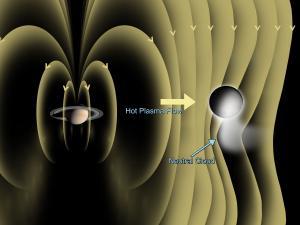
The CDA instrument found that dust kicked off by micrometeorite impacts are the source for the E-ring. Now, I should clear up some confusion brought up when comparing the atmospheric and dust results. Gas particles that make up the atmosphere appear to be generated by evaporation of warm ice or outgassing. The impact-generated cloud that forms the source of the E-ring consists of dust-sized particles, which are different from the atmosphere discussed earlier. The gases produced during a micrometorite must not be generated at a fast enough rate to be a significant contributor to Enceladus' atmosphere.